Beyond the Hype: A Practical Look at AI Adoption in the Real World
In the ever-evolving landscape of technological advancement, businesses are witnessing an unprecedented acceleration in the adoption of new technologies. This phenomenon is particularly pronounced in the realm of artificial intelligence (AI), where breakthroughs are occurring at a breakneck pace. To thrive in this dynamic environment, business leaders must not only understand the dynamics of the technology adoption curve but also proactively position their organizations to harness the transformative power of AI to keep or gain competitive advantage.
Defining AI and the Technology Adoption Curve
Before delving into the specifics, let's establish a clear understanding of the key terms:
AI: As defined by John McCarthy, AI encompasses "the science and engineering of making intelligent machines, especially intelligent computer programs." It's about creating systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation.
R&D-to-Commercialization-to-Adoption: The journey from research and development (R&D) to commercialization to adoption represents the critical pathway by which technological innovations transition from theoretical concepts to real-world applications that create value for individuals, businesses, and society as a whole.
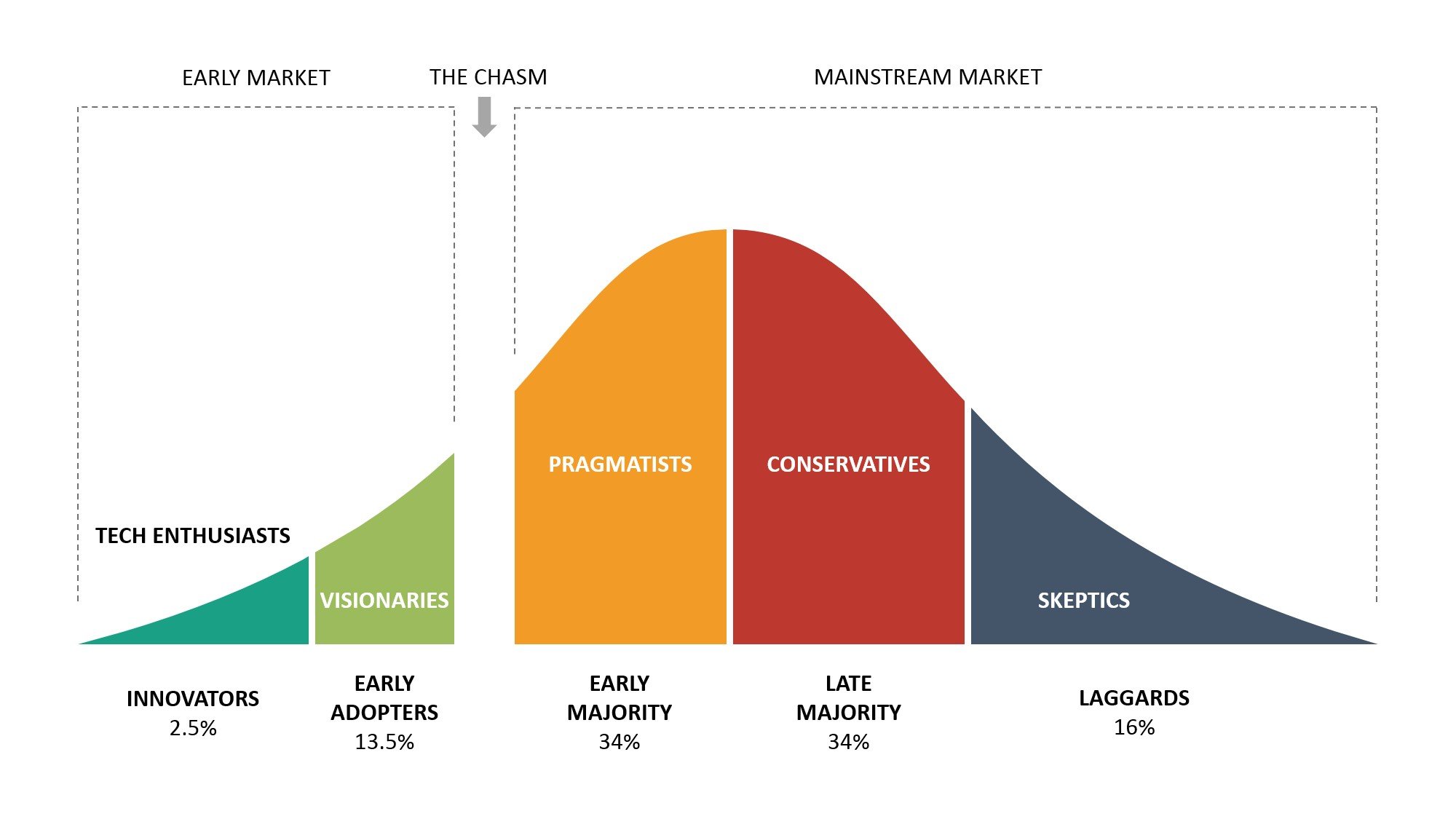
Technology Adoption Curve: This bell-shaped curve illustrates the process by which individuals and organizations adopt new technologies. It typically progresses through five distinct phases: innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, and laggards. Each phase represents a different segment of the population, with varying levels of risk tolerance, technological enthusiasm, and adoption motivations.
The Evolution of AI: From Rules-Based to Generative
The field of AI has witnessed several waves of innovation, each characterized by distinct technological paradigms and adoption patterns:
Rules-Based AI (First Wave): This initial wave relied on explicit programming and predefined rules to guide machine behavior. Think of expert systems that captured human knowledge in the form of if-then rules. While impactful in certain domains, this approach struggled with handling the complexities and ambiguities of the real world.
Machine Learning and Deep Learning (Second Wave): The second wave leveraged vast datasets and sophisticated algorithms to enable machines to learn and improve from experience. This marked a significant shift towards data-driven AI, with applications ranging from image recognition and natural language processing to recommendation systems and fraud detection. Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, further revolutionized the field with its ability to model complex patterns and relationships in data.
Generative AI (Third Wave): The third wave, powered by generative AI, represents a quantum leap in AI's potential. These models, often based on transformer architectures, can generate novel content, including text, images, and even music. They are capable of understanding and producing human-like language, opening up a vast array of possibilities across industries.
The Generational Factor in AI Adoption
A key driver of the accelerated AI adoption curve is the generational shift. Digital natives, comprising late Millennials and Gen Z, have grown up immersed in technology. They are not only comfortable with AI but also view it as an integral part of their lives. This generational fluency with technology translates into a faster and more widespread adoption of AI-powered tools and solutions.
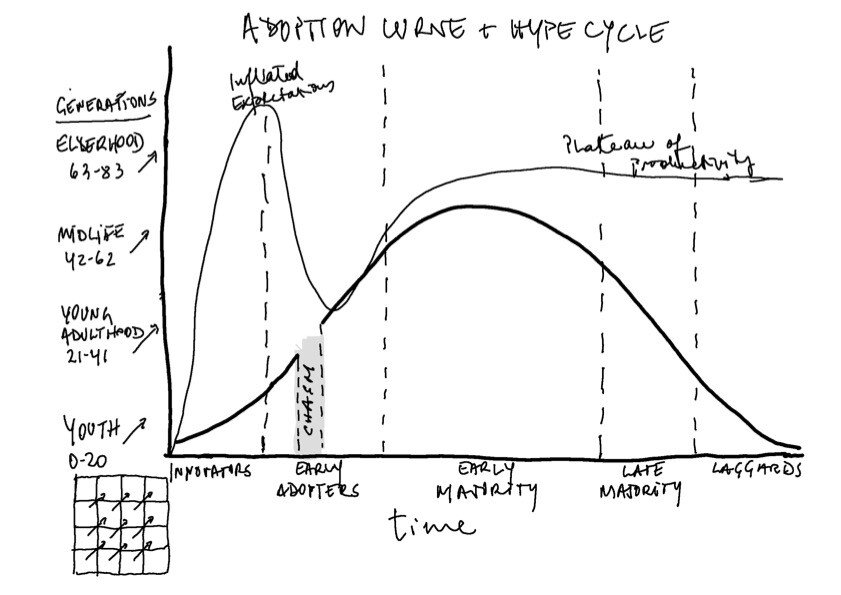
In this diagram from Renato Beninatto, he wanted to combine the Gartner Hype Cycle with the Technology Adoption Lifecycle from Geoffrey's Moore Crossing the Chasm and the Strauss-Howe generational theory. It offers an interesting perspective on exponential growth that the human brain has a hard time grasping.
Implications for Business Leaders
The rapid pace of AI adoption presents both opportunities and challenges for business leaders. To navigate this landscape successfully, consider the following:
Assess your organization's position on the adoption curve: Where do you stand in relation to your competitors? Are you an innovator, an early adopter, or lagging behind? Understanding your current position is crucial for developing a targeted AI strategy.
Identify and prioritize relevant AI technologies: Which AI applications have the potential to transform your industry and create a competitive advantage? Conduct thorough research and engage with experts to identify the most promising AI solutions for your business.
Develop a strategic AI adoption plan: Outline clear objectives, identify key stakeholders, and allocate resources effectively to ensure a smooth and successful implementation. Consider factors such as data infrastructure, talent acquisition, and change management.
Foster a culture of innovation and learning: Encourage experimentation, provide training opportunities, and empower employees to leverage AI tools to enhance their productivity and creativity. Cultivate a mindset that embraces change and views AI as an enabler rather than a threat.
Stay abreast of AI trends and developments: The AI landscape is constantly evolving. Continuous learning and adaptation are essential to remain competitive. Engage with industry thought leaders, attend conferences, and invest in ongoing education for your team.
Address ethical and societal implications: AI raises important ethical considerations, such as bias, transparency, and accountability. Proactively address these issues to build trust with customers and stakeholders.
Navigating the Chasm: From Early Adopters to the Early Majority
One of the critical challenges in technology adoption is crossing the "chasm" – the gap between early adopters and the early majority. To bridge this gap, businesses must demonstrate the tangible value and return on investment (ROI) of AI solutions. People are essential to successful AI initiatives. Conduct small pilots with key leaders and talent (even a skeptic or two) to gauge the investment that will be required in human adoption. If people are afraid that new technologies will take away their jobs, what is the incentive to adapt and innovate with new tools?
The Role of Leaders in AI Adoption
Top decision-makers play a pivotal role in exploring, learning, and considering AI adoption within organizations. Start with the direct staff, the people relied on most, to champion exploration of AI initiatives and create an environment that fosters experimentation, learning, and collaboration. Determine where an investment in AI talent, infrastructure, and education is required to ensure the organization is equipped to succeed in the AI-powered future.
Conclusion
The third wave of AI, fueled by generative technologies and accelerated by digital natives, is reshaping industries and redefining the rules of competition. Business leaders who proactively embrace AI and strategically navigate the adoption curve will position their organizations for success in this new era of technological transformation.
Remember:
The key is not just to adopt AI but to adopt it strategically and thoughtfully, aligning it with your business goals and fostering a culture that embraces innovation and change. By understanding the dynamics of the accelerated technology adoption curve and taking proactive steps to leverage AI's potential, you can unlock new opportunities for growth, efficiency, and competitive advantage.
About the Author
Tina Dao is founder and principal of Liberated Leaders, she partners with business owners and decision-makers to ease the burden of company leadership and embrace the discipline needed to create long-term value.
Tina has completed course work from MIT specific to AI and business strategy and worked in the technology industry for over 20 years in some of the most innovative companies of our era. Find out more about Tina on our About page.
Note: This blog was 85% human generated and 15% machine (AI) generated.
Citations:
The Complex Journey of Technology Adoption
Artificial Intelligence vs. Machine Learning. What is AI/ML in simple words?